As Retirement account contributions take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with American high school hip style into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. From understanding why retirement account contributions are crucial to exploring different types of accounts and investment options, this guide is your go-to for securing a financially stable future.
Importance of Retirement Account Contributions
Planning for retirement is crucial to ensure financial stability in the future. One key aspect of this planning is making regular contributions to a retirement account.
Long-Term Financial Security
- Contributing to a retirement account allows individuals to build a nest egg that can support them during their retirement years.
- By investing in a retirement account, individuals can benefit from compound interest, which helps their savings grow over time.
- Having a retirement account in place provides a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that there are funds set aside for the future.
Tax Planning and Reduced Taxable Income
- Contributions to certain retirement accounts, such as a traditional 401(k) or IRA, are often tax-deductible, reducing taxable income for the year.
- Investing in retirement accounts can help individuals lower their overall tax liability, allowing them to keep more of their hard-earned money.
- Withdrawals from retirement accounts in retirement may be taxed at a lower rate, providing additional tax benefits in the future.
Types of Retirement Accounts
When it comes to saving for retirement, there are various types of retirement accounts to choose from. Each type has its own set of rules, benefits, and eligibility criteria. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of retirement accounts:
401(k) Retirement Account
- A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement account where employees can contribute a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis.
- Employers may also match a certain percentage of the employee’s contributions, which is essentially free money towards retirement.
- Eligibility criteria typically include working for the employer for a certain period of time before being able to participate in the 401(k) plan.
Traditional IRA
- A Traditional IRA is an individual retirement account where individuals can contribute pre-tax income, allowing for tax-deferred growth until withdrawals are made during retirement.
- Contributions to a Traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, depending on income level and participation in an employer-sponsored retirement plan.
- Eligibility criteria include age limits and income thresholds for contributions.
Roth IRA
- A Roth IRA is another type of individual retirement account where contributions are made with after-tax income, but withdrawals during retirement are tax-free.
- Roth IRAs offer more flexibility with contributions and withdrawals compared to Traditional IRAs.
- Eligibility criteria for Roth IRAs include income limits based on tax filing status.
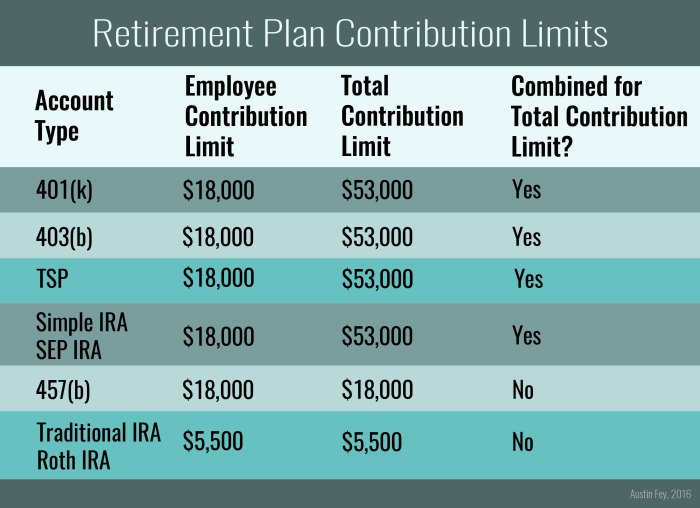
Contribution Limits and Guidelines
When it comes to contributing to your retirement account, there are specific limits and guidelines you need to be aware of to ensure you are maximizing your savings while staying within legal boundaries.
Annual Contribution Limits
- For 2021, the annual contribution limit for 401(k) plans is $19,500 for those under 50 years old. If you are over 50, you can make catch-up contributions of an additional $6,500, bringing the total limit to $26,000.
- For Traditional and Roth IRAs, the contribution limit for 2021 is $6,000 for those under 50, with a catch-up contribution of $1,000 for individuals over 50.
- For SEP IRAs, the contribution limit is based on a percentage of your income, with a maximum of $58,000 for 2021.
Penalties for Exceeding Limits
- If you contribute more than the annual limit to your retirement account, you may face penalties from the IRS. For 401(k) plans, the excess amount will be taxed at your regular income tax rate, plus a 10% penalty if withdrawn before age 59 ½.
- For IRAs, the penalty for exceeding contribution limits is 6% of the excess contribution amount each year until corrected.
Maximizing Contributions Strategies
- Set up automatic contributions from your paycheck to ensure you are consistently saving.
- Take advantage of employer matching contributions to boost your savings.
- Consider contributing windfalls, such as bonuses or tax refunds, to your retirement account.
- Regularly review your contributions and adjust them as needed to stay on track with your retirement goals.
Employer Matching Contributions
Employer matching contributions are a great way to supercharge your retirement savings. This benefit is offered by many employers as part of a retirement plan, where the employer matches a certain percentage of the employee’s contributions to their retirement account.
How Employer Matching Contributions Work
Employer matching contributions typically follow a specific formula, such as matching 50% of the employee’s contributions up to a certain percentage of their salary. For example, if an employee contributes 6% of their salary to their retirement account, the employer may match that contribution with 50%, bringing the total contribution to 9% of the employee’s salary.
Importance of Maximizing Employer Matching Contributions
Maximizing employer matching contributions is crucial because it’s essentially free money. By contributing enough to meet the employer’s matching percentage, you’re doubling your retirement savings without any additional effort. Failing to maximize this benefit is like leaving money on the table.
Examples of Accelerating Retirement Savings
For instance, let’s say your annual salary is $50,000 and your employer offers to match 50% of your contributions up to 6% of your salary. If you contribute the full 6%, which amounts to $3,000, your employer will contribute an additional $1,500. This means you’re effectively saving $4,500 towards retirement while only contributing $3,000 from your own pocket.
Investment Options for Retirement Accounts
When it comes to retirement accounts, choosing the right investment options is crucial for building a secure financial future. Let’s explore the different investment options available within retirement accounts, the importance of diversification, and tips for selecting appropriate investments based on your risk tolerance and retirement goals.
Types of Investment Options
- Stocks: Investing in individual stocks or mutual funds can offer the potential for high returns but also come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Bonds are considered safer investments than stocks and can provide a steady stream of income.
- Real Estate: Investing in real estate through real estate investment trusts (REITs) can offer diversification and potential for growth.
- Target-Date Funds: These funds automatically adjust the asset allocation based on your target retirement date, making them a convenient option for hands-off investors.
The Importance of Diversification
Diversification is key to reducing risk in your retirement account investments. By spreading your investments across different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can help protect your portfolio from market volatility and potential losses.
Tips for Selecting Investment Options
- Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Consider how much risk you are willing to take on and choose investments that align with your comfort level.
- Set Clear Goals: Define your retirement goals and time horizon to determine the right mix of investments to help you reach them.
- Review and Rebalance: Regularly review your investment portfolio and make adjustments as needed to ensure it remains in line with your goals and risk tolerance.
Impact of Retirement Account Contributions on Retirement Age
When it comes to retirement planning, the level of contributions you make to your retirement account can have a significant impact on the age at which you can retire. By understanding how varying contribution levels affect your retirement age, you can better plan for your financial future.
Early Retirement Goals
Early retirement is a goal for many individuals who wish to leave the workforce before the traditional retirement age. By increasing your retirement account contributions, you can potentially achieve early retirement by building a larger nest egg that can support you during your retirement years.
- Increasing your contributions by just a small percentage each year can have a substantial impact on your retirement age. For example, if you increase your contributions by 1% annually, you could potentially retire several years earlier than if you maintained the same contribution level.
- Setting specific savings milestones based on your contribution levels can help you track your progress towards your retirement goals. For instance, if you aim to save a certain amount by a certain age, increasing your contributions can help you reach that milestone sooner.
- By consistently contributing to your retirement account and taking advantage of compounding interest, you can accelerate your retirement savings growth and potentially retire earlier than you originally planned.
