Diving into the world of real estate investment strategies opens up a realm of possibilities and opportunities for financial growth. From buy and hold to fix and flip strategies, each approach offers a unique path to success in the real estate market. Let’s explore the ins and outs of these strategies and how they can shape your investment journey.
Real Estate Investment Strategies
Investing in real estate involves purchasing, owning, managing, renting, or selling properties for profit. It can be a lucrative way to build wealth over time and diversify an investment portfolio.
Different Types of Real Estate Investment Strategies
- Flipping Properties: Buying properties at a low price, renovating them, and selling them at a higher price for a quick profit.
- Rental Properties: Purchasing properties to rent out to tenants, generating rental income and potential appreciation in property value.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Investing in companies that own, operate, or finance income-generating real estate across a range of property sectors.
- Real Estate Crowdfunding: Pooling funds with other investors to invest in real estate projects, typically through online platforms.
The Importance of Having a Solid Investment Strategy in Real Estate
Having a well-defined investment strategy is crucial in real estate to maximize returns and minimize risks. It helps investors set clear goals, identify suitable properties, and make informed decisions based on market conditions. A solid strategy can also provide a roadmap for long-term success in the real estate market.
Buy and Hold Strategy
The buy and hold strategy in real estate investing involves purchasing properties with the intention of holding onto them for an extended period of time, typically years or even decades. The goal is to generate passive income through rental payments and benefit from property appreciation over time.
Examples of Properties Suitable for Buy and Hold Strategy
- Residential rental properties in high-demand areas with strong job markets and population growth.
- Commercial properties with stable long-term tenants and consistent cash flow.
- Vacation rental properties in popular tourist destinations with year-round demand.
Long-Term Benefits of Implementing a Buy and Hold Strategy
- Building wealth through property appreciation over time as real estate values increase.
- Generating steady passive income through rental payments, providing financial security and stability.
- Tax advantages such as depreciation deductions, mortgage interest deductions, and potential capital gains tax benefits in the long run.
Fix and Flip Strategy
Investors use the fix and flip strategy in real estate to purchase properties, renovate them, and sell them at a higher price to make a profit. This strategy involves finding properties that are undervalued or in need of repair, fixing them up to increase their value, and then selling them quickly for a profit.
Process Involved in a Fix and Flip Strategy
- Find a property: Investors need to identify properties that have potential for renovation and are priced below market value.
- Assess the property: Conduct a thorough inspection to determine the extent of repairs needed and estimate the renovation costs.
- Create a budget: Develop a budget for the renovation work, including materials, labor, and any other expenses.
- Renovate the property: Complete the necessary repairs and upgrades to increase the property’s value and appeal to potential buyers.
- Market the property: Once the renovations are complete, list the property for sale and work on attracting potential buyers.
- Sell the property: Close the sale and collect the profits from the difference between the purchase price, renovation costs, and selling price.
Risks and Rewards of Fix and Flip Strategies
- Risks:
- Market fluctuations can impact the selling price of the property.
- Unexpected repair costs can eat into the profit margin.
- The property may take longer to sell than anticipated, tying up capital.
- Rewards:
- Potential for high returns on investment in a short period of time.
- Opportunity to add value to a property and increase its resale value significantly.
- Ability to leverage renovation skills and market knowledge for profit.
Rental Property Investing
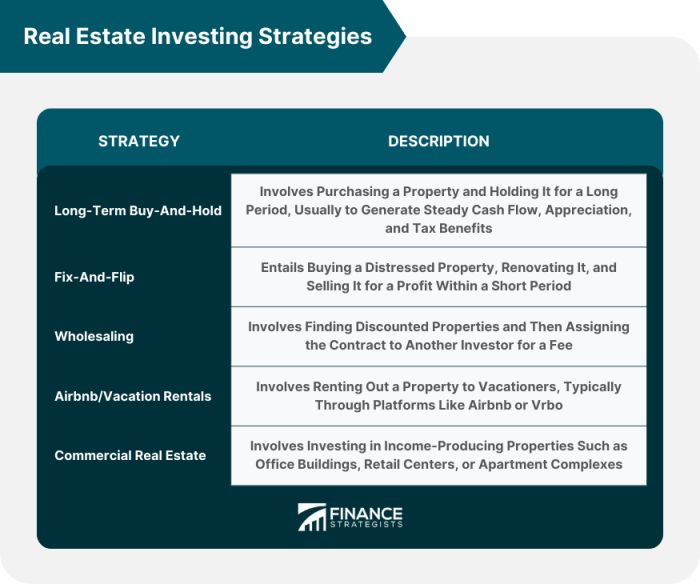
Investing in rental properties can be a great way to generate passive income and build wealth over time. By purchasing a property and renting it out to tenants, investors can benefit from regular rental payments, potential property appreciation, and tax advantages.
Benefits of Investing in Rental Properties
- Steady Income: Rental properties can provide a consistent stream of income through monthly rent payments.
- Property Appreciation: Over time, real estate properties tend to increase in value, allowing investors to build equity.
- Tax Advantages: Rental property owners can benefit from tax deductions on mortgage interest, property taxes, maintenance costs, and more.
- Diversification: Real estate investments can help diversify a portfolio and reduce risk.
Tips for Successful Rental Property Investments
- Research the Market: Understand the local rental market, vacancy rates, and rental demand in the area.
- Calculate Expenses: Consider all expenses, including mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, maintenance costs, and property management fees.
- Screen Tenants Carefully: Conduct thorough background checks and credit screenings to find reliable tenants.
- Maintain the Property: Regular maintenance and repairs can help preserve the value of the property and keep tenants satisfied.
Calculating Potential Rental Income and Expenses
To calculate potential rental income, take the monthly rent amount and multiply it by the number of months in a year. Subtract any estimated vacancy rate to get a more realistic income projection.
Potential Rental Income = Monthly Rent x 12 months – (Monthly Rent x 12 months x Vacancy Rate)
When calculating expenses, include mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, property management fees, maintenance costs, and any other relevant expenses. Deduct total expenses from the potential rental income to determine the cash flow from the investment property.
Cash Flow = Potential Rental Income – Total Expenses
Consider these calculations when evaluating the financial viability of a rental property investment.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across a range of property sectors. Investors can buy shares in publicly traded REITs, which offer a way to invest in real estate without having to buy, manage, or finance any properties themselves. REITs are required by law to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends, making them a popular choice for income-focused investors.
Definition and Functionality of REITs
REITs work by pooling funds from investors to purchase and manage a portfolio of real estate properties. These properties generate rental income, which is then distributed to shareholders as dividends. By investing in REITs, individuals can gain exposure to a diversified real estate portfolio without the need for large capital investments or the responsibilities of property management.
Investing in REITs vs. Owning Physical Properties
- Investing in REITs:
- Pros:
- Diversification: REITs offer exposure to various real estate sectors and properties, reducing risk.
- Liquidity: Shares of REITs can be bought and sold on the stock exchange, providing liquidity that owning physical properties does not offer.
- Professional Management: REITs are managed by experienced professionals, relieving investors of the burden of property management.
- Cons:
- Lack of Control: Investors have no control over the specific properties owned by the REIT or their management decisions.
- Tax Treatment: Dividends received from REITs are taxed as ordinary income, which may result in higher tax liabilities for some investors.
- Pros:
- Owning Physical Properties:
- Pros:
- Potential for Higher Returns: Direct ownership of properties may yield higher returns through appreciation and rental income.
- Tax Benefits: Property owners may benefit from tax deductions, depreciation, and other tax advantages not available to REIT investors.
- Cons:
- Capital Intensive: Buying and maintaining physical properties require significant capital investments and ongoing expenses.
- Management Responsibilities: Property owners are responsible for property management, tenant relations, and maintenance.
- Pros:
Pros and Cons of Investing in REITs
- Pros:
- Accessibility: REITs provide a low-cost and convenient way for individual investors to gain exposure to real estate markets.
- Diversification: By investing in a REIT, individuals can access a diversified portfolio of properties across different sectors and locations.
- Income Generation: REITs typically offer attractive dividend yields, making them a popular choice for income-seeking investors.
- Cons:
- Market Risk: REITs are subject to market fluctuations and interest rate changes, which can impact their performance and share prices.
- Tax Treatment: Dividends from REITs are taxed as ordinary income, potentially leading to higher tax liabilities for investors.
- Lack of Control: Investors have no say in the management or decision-making processes of the properties owned by the REIT.
