Diving into the world of leveraging debt, this introduction sets the stage for a dynamic exploration of financial strategies that can propel individuals and businesses to new heights. From understanding the concept to strategizing effectively, this guide is your gateway to mastering the art of leveraging debt.
As we delve deeper, we’ll uncover the various types of debt instruments, discuss successful leveraging strategies, and analyze the impact of leveraging debt on financial standing. Get ready to revolutionize your financial approach with these insights.
Understanding Debt Leverage
Debt leverage is a financial strategy where individuals or businesses borrow funds to invest or expand their operations, with the goal of generating higher returns than the cost of borrowing. It involves using borrowed money to increase the potential return on investment.
Examples of Debt Leverage
- Real Estate Investment: A real estate investor may use leverage by taking out a mortgage to purchase a property. If the property appreciates in value, the investor can sell it for a profit, exceeding the initial cost of borrowing.
- Business Expansion: A company may leverage debt to finance expansion projects or new product development. By investing borrowed funds strategically, the business can grow its operations and increase profitability.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
- Risk: Increased Financial Obligations – Using leverage means taking on debt, which comes with interest payments and repayment schedules. If the investments do not generate sufficient returns, it can lead to financial strain.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough financial analysis before leveraging debt, ensuring that potential returns outweigh the costs of borrowing. Develop a repayment plan and consider different scenarios to prepare for unexpected challenges.
- Risk: Market Volatility – Economic fluctuations can impact the value of investments, affecting the ability to repay borrowed funds. A sudden downturn in the market can lead to losses and financial instability.
- Mitigation: Diversify investments to reduce risk exposure and protect against market volatility. Monitor market trends closely and be prepared to adjust investment strategies based on changing conditions.
Types of Debt for Leverage
When it comes to leveraging debt, it’s essential to understand the different types of debt instruments available for this purpose. Choosing the right type of debt can significantly impact the success of your leveraging strategy. Let’s delve into the various types of debt and their suitability for leverage.
Secured vs. Unsecured Debt
Secured Debt:
– Secured debt is backed by collateral, such as real estate or equipment.
– Lenders have a claim on the collateral if the borrower defaults on the loan.
– Interest rates on secured debt are typically lower due to the reduced risk for lenders.
– Examples of secured debt include mortgages and auto loans.
Unsecured Debt:
– Unsecured debt does not require any collateral to secure the loan.
– Lenders rely solely on the borrower’s creditworthiness to determine approval and interest rates.
– Interest rates on unsecured debt are generally higher than secured debt.
– Examples of unsecured debt include credit cards and personal loans.
Choosing the Right Type of Debt:
– The decision between secured and unsecured debt depends on your financial situation and risk tolerance.
– Secured debt may offer lower interest rates but carries the risk of losing collateral if you default.
– Unsecured debt provides more flexibility but comes with higher interest rates and potential credit score implications.
– It’s crucial to assess your financial goals and risk tolerance before deciding on the type of debt to leverage.
Strategies for Leveraging Debt
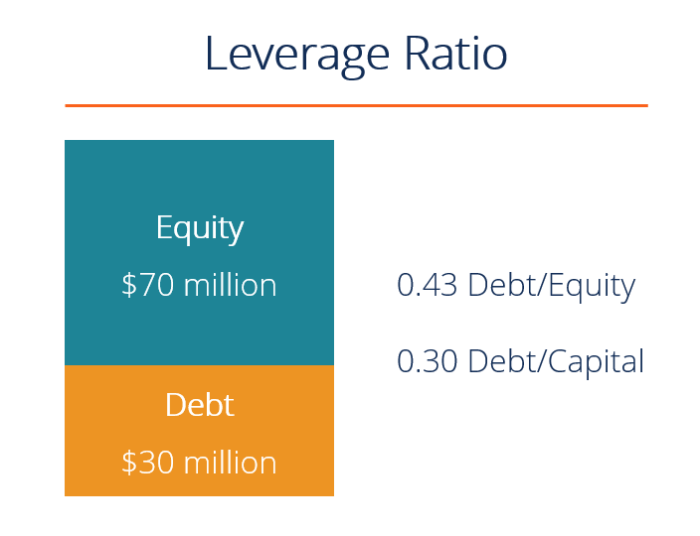
When it comes to leveraging debt, there are several strategies that can be employed to maximize returns and achieve financial goals. By utilizing debt in a strategic and responsible manner, companies and investors can leverage their resources to grow and expand their operations.
Diversification of Debt
One effective strategy for leveraging debt is to diversify the types of debt used. By spreading out debt across different sources and structures, companies can reduce risk and take advantage of varying interest rates and terms.
Debt Refinancing
Another common strategy is debt refinancing, where companies replace existing debt with new debt that has better terms or lower interest rates. This can help lower overall borrowing costs and improve cash flow.
Asset-Based Lending
Asset-based lending is a strategy where companies use their assets, such as inventory or accounts receivable, as collateral to secure loans. This can provide access to financing that might not otherwise be available and can help companies leverage their assets to grow their business.
Debt-Equity Swaps
Debt-equity swaps involve converting debt into equity, giving lenders ownership stakes in the company in exchange for forgiving or restructuring debt. This can help reduce debt levels and improve the company’s financial position.
Structured Debt Plans
Creating a structured debt plan is crucial for leveraging debt responsibly. This involves setting clear goals, assessing risk, and developing a repayment strategy to ensure that debt is managed effectively and used to achieve long-term financial success.
Impact of Leveraging Debt
When a company decides to leverage debt, it can have both positive and negative impacts on its financial position. Let’s delve into how leveraging debt affects financial statements, credit ratings, borrowing capacity, and overall business operations.
Financial Statements and Ratios
Leveraging debt can significantly impact a company’s financial statements and ratios. By taking on debt, a company increases its liabilities, which can lead to higher interest expenses and debt repayments. This, in turn, can lower the company’s profitability ratios such as return on equity (ROE) and return on assets (ROA). Additionally, high debt levels can affect the company’s liquidity ratios, making it harder to meet short-term obligations.
Credit Ratings and Borrowing Capacity
When a company leverages debt, it can impact its credit ratings and borrowing capacity. High levels of debt can signal to creditors that the company may have trouble meeting its financial obligations in the future, leading to a lower credit rating. A lower credit rating can result in higher interest rates on future borrowing, making it more expensive for the company to access credit. Additionally, excessive debt can limit a company’s ability to borrow more money in the future, potentially hindering its growth opportunities.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
To illustrate the outcomes of leveraging debt, let’s look at a real-life example. Retail giant XYZ Company decided to take on significant debt to finance an expansion project. While the expansion led to increased revenue, the company struggled to manage its debt payments, leading to a decline in profitability and a downgrade in its credit rating. As a result, XYZ Company had to cut costs and restructure its debt to avoid bankruptcy. This case highlights the importance of carefully managing debt levels to avoid negative consequences on the business.
