Diving into Financial regulations in the U.S., this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with an American high school hip style that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence.
The next paragraph provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
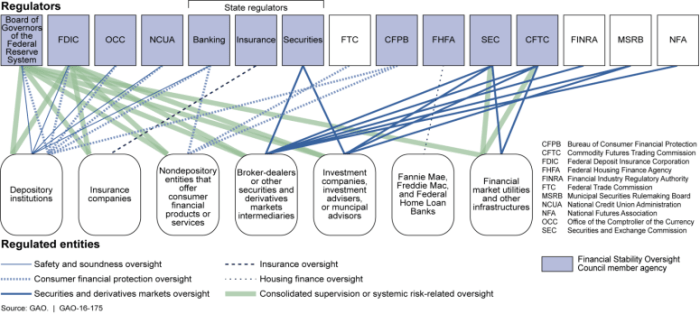
Overview of Financial Regulations in the U.S.
Yo, let’s break it down – financial regulations in the U.S. are like the rules that keep the financial system in check, making sure things run smoothly and prevent any chaos.
Key Regulatory Bodies
Check it, we got some heavy hitters overseeing the financial institutions:
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) – they regulate the securities industry, making sure investors are protected and markets are fair.
- The Federal Reserve – these folks handle monetary policy, making sure the economy stays stable.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) – they’re all about protecting consumers from shady practices in the financial world.
Evolution of Financial Regulations
Back in the day, financial regulations weren’t as tight as now. After the Great Depression hit in the 1930s, the government stepped in to prevent it from happening again. That’s when we got the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Banking Act of 1933, setting the stage for a more regulated financial system.
The Role of the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission)
When it comes to financial regulations in the U.S., the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a crucial role in ensuring fair and transparent markets. Let’s dive into the functions, responsibilities, and key regulations enforced by the SEC.
Functions and Responsibilities of the SEC
The SEC is primarily responsible for regulating the securities industry, which includes securities exchanges, brokers, and investment advisors. Some of its key functions and responsibilities include:
- Enforcing federal securities laws
- Overseeing securities transactions on stock exchanges
- Protecting investors from fraudulent activities
- Providing transparency in financial markets
Key Regulations Enforced by the SEC
The SEC enforces various regulations to maintain the integrity of the securities market. Some of the key regulations enforced by the SEC include:
- The Securities Act of 1933
- The Securities Exchange Act of 1934
- The Investment Company Act of 1940
- The Investment Advisers Act of 1940
Comparison to Other Regulatory Bodies
While the SEC focuses on regulating the securities industry, other regulatory bodies oversee different aspects of the financial sector. A key comparison can be made between the SEC and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), which regulates the futures and options markets. Both agencies work to maintain market integrity and protect investors, but they have distinct areas of focus within the financial sector.
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, commonly known as Dodd-Frank, was enacted in 2010 in response to the 2008 financial crisis. The main objectives of the Act were to promote financial stability, protect consumers, and reduce the risk of another economic meltdown.
Impact on Financial Institutions and Consumers
- Dodd-Frank imposed stricter regulations on financial institutions, such as banks, to prevent excessive risk-taking and ensure they have enough capital to cover potential losses.
- The Act created the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) to oversee consumer financial products and services, protecting consumers from abusive practices.
- It introduced the Volcker Rule, which prohibits banks from engaging in certain types of speculative trading that do not benefit their customers.
Effectiveness in Preventing Another Financial Crisis
- Some argue that Dodd-Frank has been successful in increasing transparency and accountability in the financial sector, reducing the likelihood of another crisis.
- However, critics claim that the Act has placed excessive regulatory burdens on financial institutions, potentially stifling economic growth.
- Overall, the effectiveness of Dodd-Frank in preventing another financial crisis remains a topic of debate among policymakers and economists.
Compliance and Enforcement of Financial Regulations
Financial regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and integrity of the financial system in the United States. Compliance with these regulations is essential for financial institutions to maintain transparency and accountability in their operations.
Compliance for Financial Institutions
- Financial institutions are required to adhere to a set of rules and guidelines established by regulatory bodies such as the SEC and the Federal Reserve.
- Compliance involves implementing internal controls, conducting regular audits, and reporting financial information accurately and timely.
- Failure to comply with regulations can result in severe consequences, including fines, sanctions, and legal actions.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Financial institutions that fail to comply with regulations may face monetary penalties imposed by regulatory agencies.
- In some cases, individuals responsible for non-compliance may also be subject to criminal charges and imprisonment.
- Penalties for non-compliance are designed to deter misconduct and protect investors and consumers from fraudulent activities.
High-Profile Cases of Enforcement Actions
- One notable case of enforcement action is the Wells Fargo account scandal, where the bank opened millions of unauthorized accounts without customers’ consent, leading to a $185 million settlement with regulators.
- Another high-profile case is the insider trading charges against hedge fund manager Raj Rajaratnam, resulting in a record-breaking $92.8 million civil penalty.
- The Enron scandal in the early 2000s also led to the enactment of stricter regulations such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to prevent corporate fraud and enhance financial transparency.
