Diving deep into the world of asset allocation strategies, this guide will take you on a journey exploring the ins and outs of this crucial investment approach. From understanding the key components to implementing effective strategies, get ready to level up your investment game!
Overview of Asset Allocation Strategies
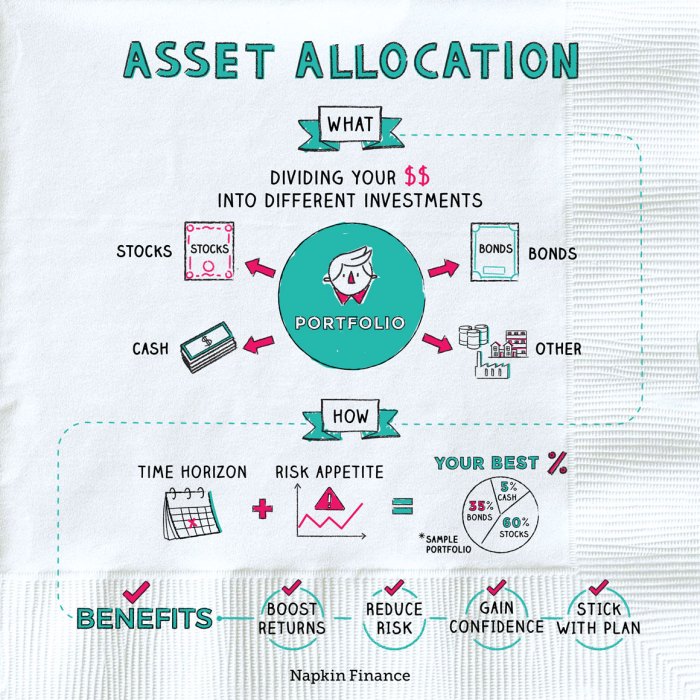
Asset allocation strategies are crucial techniques used in investment to distribute funds among different asset classes to achieve a balance between risk and return. By diversifying investments across various asset classes, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolio while maximizing potential returns.
Key Components of Asset Allocation Strategies
- Asset Classes: Asset allocation involves dividing investments into different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash equivalents.
- Risk Tolerance: Understanding your risk tolerance is essential in determining the mix of assets in your portfolio.
- Investment Goals: Identifying your investment goals, whether it’s long-term growth, income generation, or capital preservation, helps in selecting the right asset allocation strategy.
- Time Horizon: The time horizon for your investments plays a significant role in determining the allocation of assets.
Examples of Different Asset Classes
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing regular interest income with lower risk compared to stocks.
- Real Estate: Investments in physical properties like residential or commercial real estate, offering diversification and potential for rental income.
- Cash Equivalents: Highly liquid and low-risk investments like money market funds or treasury bills, providing stability to the portfolio.
Types of Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to asset allocation strategies, there are several approaches that investors can take to manage their portfolios effectively. Let’s explore the key differences between strategic, tactical, and dynamic asset allocation strategies, as well as the comparison between passive and active strategies, and the concept of rebalancing.
Strategic, Tactical, and Dynamic Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies can generally be categorized into three main types: strategic, tactical, and dynamic. Each approach has its own unique characteristics and is suited to different investment goals and risk profiles.
- Strategic Asset Allocation: Involves setting a target allocation of assets based on long-term financial goals and risk tolerance. This strategy typically requires periodic rebalancing to maintain the desired asset mix.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Involves actively adjusting the portfolio’s asset allocation based on short-term market conditions or opportunities. This strategy aims to capitalize on market trends and may involve more frequent trading.
- Dynamic Asset Allocation: Combines elements of both strategic and tactical approaches by allowing for shifts in asset allocation based on predefined parameters or market indicators. This strategy offers flexibility in responding to changing market conditions.
Passive vs. Active Asset Allocation Strategies
Another important distinction in asset allocation strategies is between passive and active approaches. Here’s how they differ:
- Passive Asset Allocation: Involves maintaining a fixed asset allocation according to a predetermined strategy without frequent adjustments. This approach aims to minimize costs and relies on long-term market trends.
- Active Asset Allocation: Involves making frequent adjustments to the asset allocation in response to changing market conditions or opportunities. This approach seeks to outperform the market through strategic shifts in asset allocation.
Rebalancing in Asset Allocation Strategies
Rebalancing is a crucial aspect of asset allocation strategies that involves periodically adjusting the portfolio back to its target asset allocation. This process helps maintain the desired risk-return profile and ensures that the portfolio remains aligned with the investor’s financial goals.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation Decisions
When it comes to making decisions about asset allocation, investors take into account several key factors that can impact their choices. These factors play a crucial role in shaping their investment strategies and determining the mix of assets in their portfolios.
Risk tolerance is a critical factor that investors consider when deciding on asset allocation. This refers to an individual’s willingness and ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to riskier assets, such as stocks, in pursuit of potentially higher returns. On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach, with a higher allocation to safer assets like bonds.
Another important factor that influences asset allocation decisions is investment goals. Investors typically have specific financial objectives they aim to achieve through their investments, such as saving for retirement, funding education expenses, or purchasing a home. These goals can vary in terms of time horizon and desired outcomes, impacting the mix of assets chosen to align with these objectives.
The time horizon of an investor also plays a significant role in asset allocation decisions. The length of time an investor has to reach their financial goals can influence the level of risk they are willing to take. For example, investors with a longer time horizon may be more inclined to allocate a higher percentage of their portfolio to equities, as they have more time to ride out market fluctuations and benefit from the potential long-term growth of stocks.
In summary, factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon are key considerations that investors take into account when determining their asset allocation strategies. By carefully evaluating these factors, investors can create a well-balanced portfolio that aligns with their individual financial objectives and risk preferences.
Implementing Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to implementing asset allocation strategies, the key is to construct a well-diversified portfolio that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance. This involves spreading your investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash equivalents.
Constructing a Well-Diversified Portfolio
Constructing a well-diversified portfolio through asset allocation requires careful consideration of your financial goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. By spreading your investments across various asset classes, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your overall portfolio.
- Determine your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Allocate your assets across different asset classes based on your risk profile.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain diversification.
Monitoring and Adjusting Asset Allocation
Monitoring and adjusting your asset allocation over time is crucial to ensure that your portfolio remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Market conditions and your personal circumstances may change, necessitating adjustments to your asset allocation.
- Regularly review your portfolio performance and asset allocation.
- Adjust your asset allocation based on changes in market conditions or your financial goals.
- Consider working with a financial advisor to help you make informed decisions.
Tools and Resources for Implementing Asset Allocation Strategies
There are various tools and resources available to help you implement asset allocation strategies effectively. These tools can provide insights into asset allocation models, risk assessment, and portfolio management.
- Online investment platforms that offer asset allocation tools.
- Asset allocation calculators to determine the optimal mix of assets for your portfolio.
- Financial planning software to track your portfolio performance and asset allocation.
